Motors often produce noise, and it’s crucial to understand how to differentiate between normal and abnormal sounds to effectively troubleshoot. Just like a baby, a motor doesn’t explicitly communicate when something is wrong, but the noises it generates can offer valuable insights.
If a motor is making unusual noises, potential causes might include:
- Backlash
- Gear damage
- Excessive vibration
- Motor damage
- Gearhead damage
This article delves deeper into these types of noises and offers solutions to minimize them. It’s important to isolate the motor from other noise sources, such as metal plates or loose bolts. Having an extra motor in good condition for comparison can also be incredibly helpful.
Let’s explore these issues further:
### Backlash
Gear noise can arise from geared motors due to the continuous collision of gear surfaces during rotation. This noise stems from backlash, which refers to the gap between gear teeth. The sound typically resembles a consistent hum, and the nature of the noise can vary depending on the type of gears used. While this noise is generally not indicative of a malfunction, it doesn’t affect the motor's performance or the lifespan of the gearhead.
Here’s an example of a spur gear with backlash:
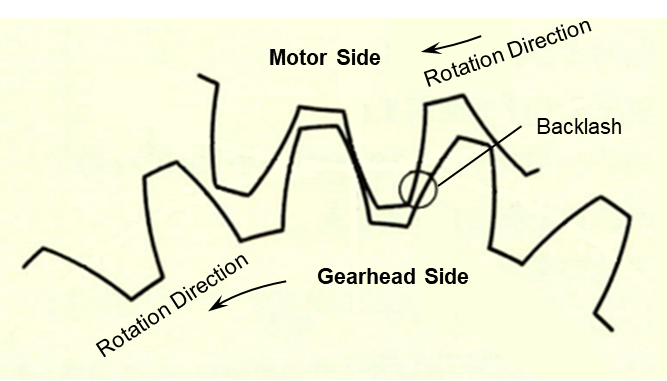
In some cases, this noise can become amplified, especially when the motor is unloaded or oversized. For AC motors, when the load is lighter than the rated load, the motor operates less efficiently, leading to increased vibration and noise. Brushless and stepper motors don’t face this issue because the driver regulates the power supply.
#### How to Verify?
This noise is usually more pronounced when the motor is unloaded. To test, apply a slight frictional load to the gearhead output shaft. If the noise diminishes under this load, it’s normal. However, if the noise persists or worsens with increased load, the cause may lie elsewhere.
For bi-directional applications, helical gears or high-quality gears with more contact surface are recommended to reduce impact sounds. For optimal performance, ensure your motor sizing consultation includes selecting both the motor and the appropriate gear type.
---
### Gears
For geared motors, any damage or scratches on the gear teeth can create abnormal noise during rotation. If you notice an increase in noise after assembling or disassembling the motor and gearhead, it’s possible that the gears have been damaged.
Oriental Motor designs its motors with a pinion shaft directly mated to the gearhead, eliminating the need for a coupling. This approach keeps the motor compact but requires extra care during assembly.

Even though the motor’s characteristics remain unaffected, scratches on the pinion shaft can cause additional noise. Unfortunately, this issue can only be resolved by replacing the gearhead.
#### How to Verify?
If the noise significantly increases when the motor and gearhead are assembled, it indicates potential damage or scratches on the gear teeth. Oriental Motor can confirm this through a product inspection, but beyond that, there isn’t much we can do.
If you hear a periodic sound at specific intervals, it may be possible to estimate which gear tooth is damaged. Be cautious when assembling or disassembling gearheads to avoid damaging the internal gears.
---
### Excessive Vibration
Vibration is a major contributor to noise. Incorrect connections or power supply voltage can amplify vibration. Higher voltages increase torque, but excessive torque can lead to increased noise. Fluctuations in voltage also alter the motor's speed-torque curve and operating temperature. Loose bolts or metal plates can further amplify vibration.
When troubleshooting noise, isolate all other potential vibration sources.
#### How to Verify?
Check the wiring between the power supply, capacitor, and motor. Ensure the input voltage falls within ±10% of the motor’s specifications. Use the correct capacitor between the power supply and motor. The rated voltage and capacitance are critical for determining the motor’s speed-torque curve, rated torque, and magnetic balance. Using incorrect values can disrupt motor efficiency and increase vibration.
Use a voltage tester to confirm the applied voltage matches the capacitor terminal voltage. For example, a motor with a rated voltage of 100 VAC might require a capacitor rated at 250 VAC.
---
### Motor Damage
If the motor shaft makes noise without the gearhead attached, there’s likely an issue with the motor itself, such as a damaged bearing due to excessive load. Mishandling, like dropping the motor, can also cause damage.
#### How to Verify?
Disconnect the motor from power and load. Inspect the pinion shaft for damage and listen for noise when rotating the shaft manually. If the shaft doesn’t rotate smoothly, the bearings may be damaged. For motors with an electromagnetic brake, release the brake before testing.
---
### Gearhead Damage
If the gearhead is noisy without the motor, it’s likely damaged—possibly the case, bearings, or gears. Accurate noise measurement and a reference point for normal noise are essential for diagnosis.
#### How to Verify?
Remove the gearhead and visually inspect the gears. Try rotating the gearhead shaft to inspect more gears. Shake the gearhead to ensure nothing feels “loose.†Attempt to rotate the shaft manually.
---
That’s all for now! Replacing the motor or gearhead is the simplest solution, but preventing these issues through proper motor sizing analysis is far better. This article provides a deeper understanding of motor noise, helping you avoid similar problems in the future.
Feel free to reach out to our technical support engineers for further assistance.
---
**FAQs**
Q: I bought the same motor and gearhead as before, but the noise during operation is louder. What could be the reasons?
A: Possible causes include:
1. Backlash noise varies with load conditions.
2. Resonance from the workpiece increases noise.
3. Scratches on the motor shaft.
Q: How do I replace a pre-assembled geared motor?
A: Follow the manual instructions carefully, ensuring proper tightening torque.
Q: How do I check compatibility between specific motors and gearheads?
A: Check part numbers or consult our technical support engineers.
Q: Can I check if an AC motor is broken?
A: Yes, measure winding resistance, check capacitor capacity, and inspect bearings manually.
---
*Disclaimer*: This article offers troubleshooting tips, but only qualified professionals should perform repairs. Contact our technical support team if unsure. Oriental Motor is not responsible for any injuries resulting from attempted repairs.
Screw Tip Assembly (Alloy Spraying, Chrome Plating, Coating)
Screw Tip Assembly (Alloy Spraying, Chrome Plating, Coating),Screw Tip,Tip Screw,Injection Molding Screw Tip